Setup
The Stabilizer firmware consists of different applications tailored to different use cases. Only one application can run on the device at a given time. After receiving the Stabilizer hardware, you will need to choose, build, and flash one of the applications onto the device.
Power
Power Stabilizer through exactly one of the following mechanisms.
- Via the backside 12V barrel connector
- Via Power-over-Ethernet using a PoE capable switch (802.3af or preferrably 802.3at) and the RJ45 front panel port
- Via an EEM connection to Kasli
Note: Applying power through more than one mechanism may lead to damage. Ensure the two unused methods are not connected or explicitly disabled.
Network and DHCP
Stabilizer supports 10Base-T or 100Base-T with Auto MDI-X.
Stabilizer uses DHCP to obtain its network configuration information. Ensure there is a properly
configured DHCP server running on the network segment that Stabilizer is connected to. If a DHCP
server is not available and a static IP is desired, Stabilizer can be configured with a static IP
via the USB interface. A configured ip of "0.0.0.0" will use DHCP.
Note: If Stabilizer is connected directly to an Ubuntu system (for example using a USB-Ethernet dongle) you can set the IPv4 settings of this Ethernet connection in the Ubuntu network settings to "Shared to other computers". This will start and configure a DHCP server for this connection.
MQTT Broker
Stabilizer requires an MQTT broker that supports MQTTv5. The MQTT broker is used to distribute and exchange elemetry data and to view/change application settings. The broker must be reachable by both the host-side applications used to interact with the application on Stabilizer and by the application running on Stabilizer. The broker must be reachable on port 1883 on that IP address - it may either be an IP address or a fully qualified domain name. Firewalls between Stabilizer and the broker may need to be configured to allow connections from Stabilizer to that port and IP address.
Mosquitto has been used as a MQTT broker during development, but any MQTTv5 broker without authentication or encryption will likely work.
Note: Mosquitto version 1 only supports MQTTv3.1. If using Mosquitto, ensure version 2.0.0 or later is used.
We recommend running Mosquitto through Docker to easily run it on
Windows, Linux, and OSX. After docker has been installed, run the following command from
the stabilizer repository to create a container named mosquitto that can be stopped
and started easily via docker:
# Bash
docker run -p 1883:1883 --name mosquitto -v `pwd`/mosquitto.conf:/mosquitto/config/mosquitto.conf -v /mosquitto/data -v /mosquitto/log eclipse-mosquitto:2
# Powershell
docker run -p 1883:1883 --name mosquitto -v ${pwd}/mosquitto.conf:/mosquitto/config/mosquitto.conf -v /mosquitto/data -v /mosquitto/log eclipse-mosquitto:2
Building
- Get and install rustup and use it to install a current stable Rust toolchain.
Stabilizer tracks stable Rust. The minimum supported Rust version (MSRV) is specified in the manifest (
Cargo.toml). - Install target support with
rustup target add thumbv7em-none-eabihf - Install cargo-binutils with
cargo install cargo-binutils; rustup component add llvm-tools-preview - Clone or download the firmware with
git clone https://github.com/quartiq/stabilizer; cd stabilizer - Build firmware with
cargo build --release - Extract the application binary (substitute
dual-iirbelow with the desired application name) withcargo objcopy --release --bin dual-iir -- -O binary dual-iir.bin
Flashing
Firmware can be loaded onto stabilizer using one of the three following methods.
Note: Most methods below require access to the circuit board. Pulling the device from a crate always requires power removal as there are sensitive leads and components on both sides of the board that may come into contact with adjacent front panels. Every access to the board also requires proper ESD precautions. Never hot-plug the device or the probe.
ST-Link virtual mass storage
If a ST-Link V2-1 or later is available this method can be used.
Power down the device, remove it from the crate, and connect the SWD/JTAG probe as shown below to the device and to your computer.
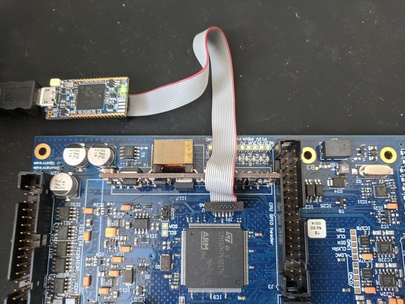
Power up the device and copy dual-iir.bin onto the virtual mass storage ST-Link drive
that has appeared on your computer.
Power down the device before removing the probe, inserting it into the crate
and applying power again.
DFU Upload
If an SWD/JTAG probe is not available, you can flash firmware using only a micro USB cable plugged in to the front of Stabilizer, and a DFU utility.
Note: If there is already newer firmware running on Stabilizer that supports the USB serial interface, there is no need to remove Stabilizer from the crate or disconnect any existing connectors/power supplies or to jumper the BOOT0 pin. Instead, open the serial port on Stabilizer and request it to enter DFU mode:
python -m serial <serial-port> > platform dfuAfter the device is in DFU mode, use the
dfu-utilcommand specified in the instructions below, and the DFU firmware update will be complete.
- Install the DFU USB tool
dfu-util - Remove power
- Then carefully remove the module from the crate to gain acccess to the board
- Short JC2/BOOT with the jumper
- Connect your computer to the Micro USB connector below/left of the RJ45 connector on the front panel
- Insert the module into the crate
- Then power it
- Perform the Device Firmware Upgrade (DFU) with
dfu-util -a 0 -s 0x08000000:leave -R -D dual-iir.bin - To keep the device from entering the bootloader remove power, pull the board from the crate, remove the JC2/BOOT jumper, insert the module into the crate, and power it again
SWD/JTAG Firmware Development
To observe logging messages or to develop and debug applications a SWD/JTAG
probe is required. To use a compatible probe with probe-run connect it as
described above.
- Install
probe-rs - Build and run firmware on the device with
cargo run --release --bin dual-iir
When using debug (non --release) mode, decrease the sampling frequency significantly.
The added error checking code and missing optimizations may lead to the application
missing timer deadlines and panicing.
USB
The USB port can be used to bootstrap Stabilizer and configure all internal settings. This is used to specify a fixed IP address, the MQTT broker address or when operating Stabilizer in standalone mode (i.e. without an ethernet connection or an MQTT broker).
Connect a USB cable and open up the serial port in a serial terminal of your choice. pyserial
provides a simple, easy-to-use terminal emulator:
python -m serial <port>
Once you have opened the port, you can use the provided menu to update any of Stabilizers runtime settings.
Note: Network settings (IP and broker) configured via USB do not take immediate effect but require a reboot.
MQTT configuration
The MQTT broker address is configured via the USB port on Stabilizer's front panel. The address can be an IP address or a domain name. Once the broker address has been updated, power cycle stabilizer to have the new broker address take effect.
Verify MQTT connection
Once your MQTT broker and Stabilizer are both running, verify that the application connects to the broker.
A Stabilizer application dual-iir on a device with MAC address ``aa-bb-cc-00-11-22is reporting its status on thedt/sinara/dual-iir/aa-bb-cc-00-11-22/alive` topic.
In addition to the alive status the application publishes meta information about itself on boot, and telemetry messages
at regular intervals. Once you observe telemetry, Stabilizer is operational.
To observe MQTT messages there are several different options. These are
Always connect to the same broker that the device is connecting to (the one set via the serial terminal connection).
CLI: mosquitto_sub
Tools from the mosquitto project:
mosquitto_sub -t 'dt/sinara/dual-iir/+/#' -h mqtt -v
TUI: mqttui
mqttui -b mqtt://mqtt/
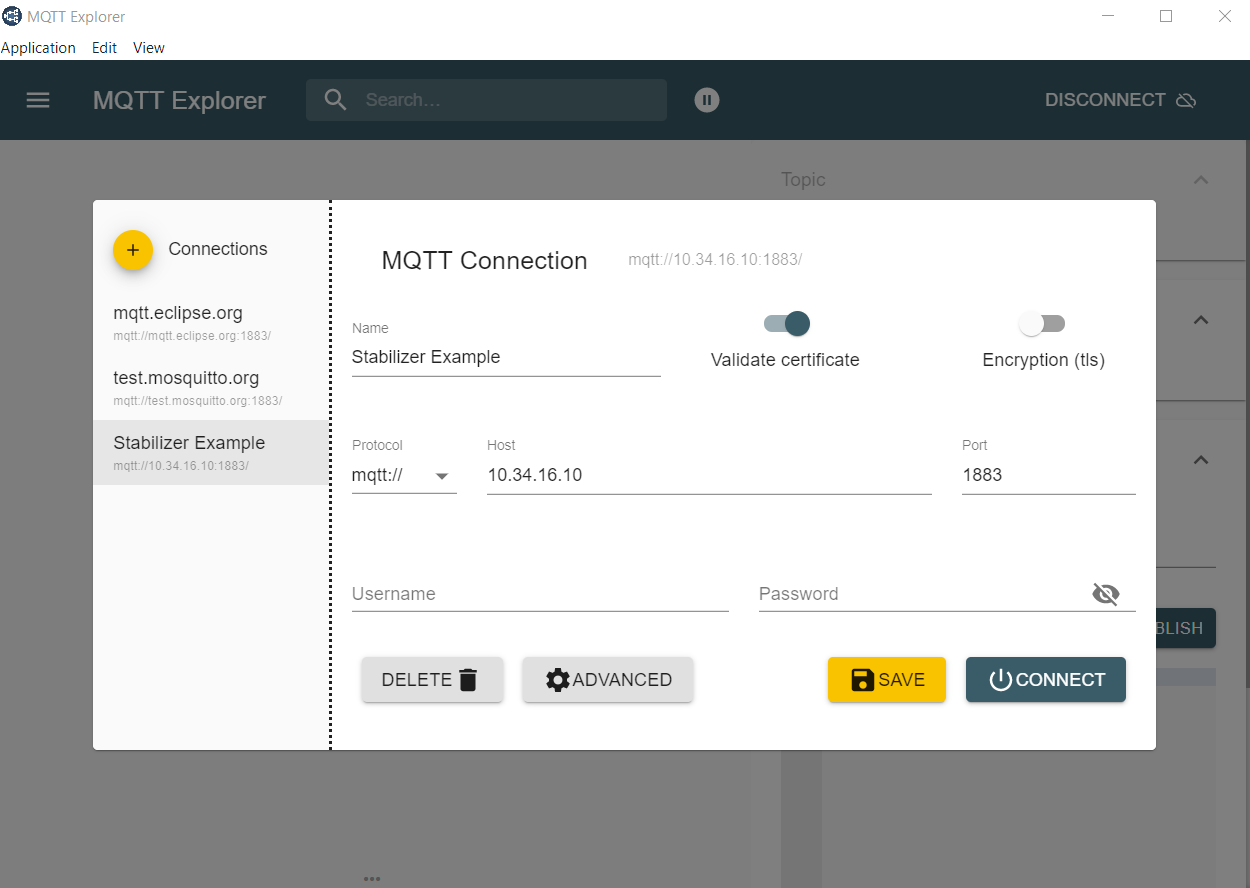
GUI: MQTT-Explorer or MQTTX
Download MQTT-Explorer to observe which topics have been posted to the Broker.
Scraping: telegraf
This telegraf configuration snippet scrapes settings, alive-ness, metadata,
and telemetry from stabilizer/booster/thermostat/thermostat-eem applications.
[[inputs.mqtt_consumer]]
alias = "miniconf"
servers = ["tcp://mqtt:1883"]
topics = [
"dt/sinara/+/+/telemetry/#",
"dt/sinara/+/+/settings/#",
"dt/sinara/+/+/alive",
"dt/sinara/+/+/meta",
]
data_format = "value"
value_field_name = "value"
data_type = "string" # utf8 json
name_override = "miniconf"
[[processors.starlark]]
alias = "miniconf"
namepass = ["miniconf"]
source = '''
load("json.star", "json")
def apply(metric):
if metric.fields["value"] == "":
return None # miniconf list/dump/get request, will
# dt/sinara/{app}/{id}/{class}[/{path}]
topic = metric.tags.pop("topic").split("/", 5)
metric.tags["id"] = topic[3]
metric.tags["class"] = topic[4]
metric.tags["path"] = "".join(topic[5:])
v = json.decode(metric.fields["value"])
if topic[4] == "telemetry":
metric.name = topic[2]
for k, v in flatten("", v):
metric.fields[k[1:]] = v
metric.fields.pop("value")
else:
metric.tags["app"] = topic[2]
t = type(v)
if t in ("float", "int", "bool", "string"):
metric.fields[t] = v
metric.fields.pop("value")
return metric
def flatten(k, v):
l = []
t = type(v)
if t == "list":
for i, vi in enumerate(v):
l.extend(flatten("%s_%d" % (k, i), vi))
elif t == "dict":
for ki, vi in v.items():
l.extend(flatten("%s_%s" % (k, ki), vi))
elif t in ("float", "int", "bool", "string"):
l.append((k, v))
return l
'''
Within telegraf the mqtt telemetry data can then be routed to e.g. influxdb, prometheus or grafana live.