Ethernet Telemetry and Control
Booster uses MQTT for telemetry reporting, settings configuration, and control of the channels. All
booster MQTT topics are prefixed with dt/sinara/booster/<ID>, where 12-34-56-78-90-ab). The ID is configurable via the USB port.
Please refer to Stabilizer's documentation for instructions on getting MQTT configured.
We recommend using mqtt-explorer to view telemetry and run-time
settings.
Measurement Units
Booster uses SI units (Volt, Ampere, Celsius) for telemetry and settings. Power measurements are specified in dBm.
Telemetry
Telemetry is generated on the
<prefix>/telemetry/ch<N> topics, where N is an integer from 0 to 7. Telemetry is only reported for
connected channels. Telemetry is transmitted in human-readable JSON format for logging purposes.
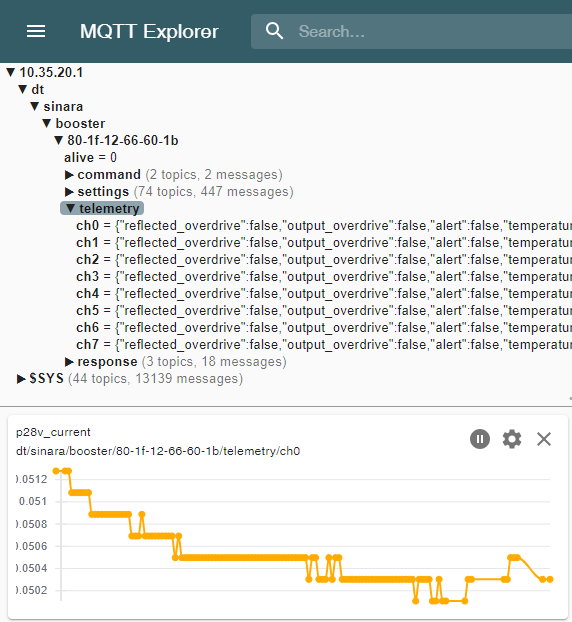
Figure 1: Example display of Booster telemetry on all 8 channels reported via MQTT Explorer.
Settings
Booster leverages miniconf to manage run-time settings and
configuration identical to Stabilizer. Please refer to Stabilizer's Miniconf
Documentation to get
started.
When settings are saved in booster, the saved channel configuration will be applied to the channel when Booster boots. Note that saving channel settings overwrites any existing channel configuration and calibrations including those from the old legacy firmware. The legacy firmware settings are incompatible.
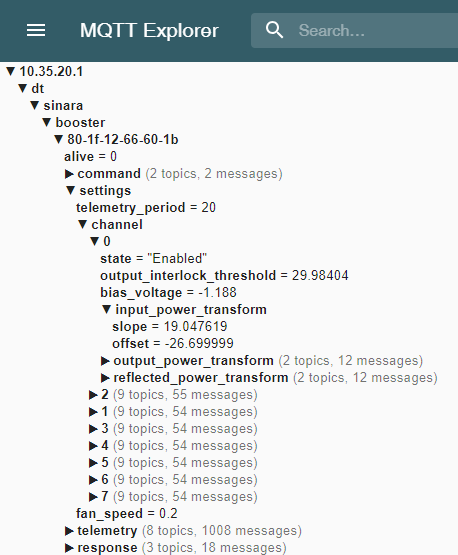
Figure 2: Example display of Booster settings tree reported via MQTT Explorer.
Control
Booster supports channel bias tuning and saving active channel settings configuration to EEPROM
via the Booster python package located in the py folder of the repository. Execute the
following to install the package and see how to use it:
pip install ./py
python -m booster --help